Main functions
Calculation
runCalcMethod()
runCalcMethod(methodID, compID); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
methodID | string | Unique ID of the calculation method to run. A list of all calculation methods can be found in the section Calculations in scripting. |
compID | int | Unique ID of the component in the model. The system calculation is always performed on the gear unit (always has ID 1). |
{options} | object | If specified, an output directory with the calculation kernel output files is created. var options = {resultpath: path/to/results, createResultpath: true/false}; |
Return value | int | 1 = calculation successful 0 = calculation terminated -1 = error in the calculation |
Possible errors | Calculation does not exist. Component does not exist. Component cannot be calculated with the specified calculation method. | |
Example 1 Perform a system calculation
1methodID = "001_SYSTEM_CALCULATION"; 2var compID = 1; 3setAttr("gta_switch_iso_6336_2006", compID, true, EDAT); 4var status = runCalcMethod(methodID, compID); 5if (status == 1) { 6 println("Calculation was successful"); } else { 7 println("Something went wrong"); }
Assigns the ID for a system calculation to the methodID variable. | |
Assigns the ID of the gear unit to the compID variable. The ID of the gear unit is always 1. | |
Uses setAttr() to set the attribute with the ID "gta_switch_iso_6336_2006" to true. This will perform a load capacity calculation according to ISO 6336 (2996) as part of system calculation. | |
Starts the system calculation and stores the return value in the status variable. | |
If the return value in the status value = 1, then: | |
Output to the scripting console: "Calculation was successful." | |
For any other return value: "Something went wrong." |
Example 2 Perform a bearing life calculation for a single bearing.
methodID = "800_ROLLING_BEARING_LIFETIME"; var compID = 15; runCalcMethod(methodID, compID);
Accessing attributes
getAttr()
getAttr(attrID, compID, EDAT/RDAT); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
attrID | string | Unique ID of the attribute. |
compID | int | Unique ID of the component in the model. |
EDAT/RDAT | Specifies whether the input (EDAT) or calculated value (RDAT) should be returned. Alternatively, 1 (EDAT) or 0 (RDAT) can be specified as a parameter. For more information, see Data integrity (EDAT/RDAT) | |
Return value | Value of the attribute. | |
Possible errors | Incorrect Attribute ID or component ID. Only for string, integer, double, boolean, array, and matrix attributes. | |
Example 1 Output the value of the normal pressure angle attribute to the console.
1let compID = getCompByType('cylindrical_mesh')[0]; 2let value = getAttr("normal pressure angle", compID, EDAT); 3println(value);
Assigns the component ID of the first cylindrical gear stage in the model to the compID variable. | |
Assigns the input value (EDAT) of the normal pressure angle attribute to the value variable. | |
Outputs the value of the variable to the Scripting Monitor. |
Example 2 Output the values of the static load rating array attribute to the console.
1let compID = getCompByType('bearing')[0]; 2let value = getAttr("static capacity", compID, RDAT); 3println(value[0]); 4println(value[1]);
Assigns the component ID of the first rolling bearing in the model to the compID variable. | |
Assigns the calculated value (RDAT) of the static capacity attribute to the value variable. static capacity is an array attribute and contains a value for every bearing row. | |
Outputs the attribute value for the first bearing row to the Scripting Monitor. | |
Outputs the attribute value for the second bearing row to the Scripting Monitor. |
setAttr()
setAttr(attrID, compID, value, EDAT/RDAT); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
attrID | string | Unique ID of the attribute. |
compID | int | Unique ID of the component in the model. |
EDAT/RDAT | Specifies whether the input (EDAT) or calculated value (RDAT) should be returned. Alternatively, 1 (EDAT) or 0 (RDAT) can be specified as a parameter. | |
Possible errors | Incorrect Attribute ID. Incorrect component ID. Data type of the value does not match the attribute. Value violates the constraints. | |
Example 1 Set the value of the oil temperature attribute to 90.
1var compID = 1; 2setAttr('temperature', compID, 90, EDAT);
Assigns the variable compID with the component ID of the gear unit. As the root component, the gear unit always has the ID of 1. | |
Assigns the attribute temperature of component 1 with the input value (EDAT). |
Example 2 Set the attribute FVA_54 to true. The attribute FVA_54 corresponds to the "Calculation of micro pitting acc. to FVA 54" switch in the input editor.
1var compID = getCompByType('cylindrical_mesh')[0]; 2setAttr('FVA_54', compID, true, EDAT);
delAttr()
delAttr(attrID, compID); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
attrID | string | Unique ID of the attribute. |
compID | int | Unique ID of the component in the model. |
Return value | boolean | true if value deleted, otherwise false. |
Possible errors | Incorrect component ID. Incorrect attribute ID. | |
Example 1 Delete the lubricant attribute of the gear unit.
1delAttr('lubricant', 1);Deletes the lubricant for the component gear unit. |
getAttrProperty()
getAttrProperty(attrID, compID, propertyID); | |||
Parameter | Type | Description | |
attrID | string | Unique ID of the attribute in the model. | |
compID | int | Unique ID of the component in the model. | |
propertyID | string | TYPE | Data type of the attribute. |
NUMBER | Numeric attribute ID. | ||
NAME | Attribute name | ||
UNIT_NAME | Unit | ||
SYMBOL | Symbol | ||
EDAT_VALUE | EDAT value converted to string. | ||
RDAT_VALUE | RDAT value converted to string. | ||
Return value | Property of the attribute in the language in which the FVA-Workbench was started. | ||
Possible errors | Incorrect component ID Incorrect attribute ID Attribute and component ID do not match. | ||
Example Query the properties of the "face width" attribute on a cylindrical gear with ID 8.
1var compID = 8; 2var attributeID = 'face width'; 3println('Name: ' + getAttrProperty(attributeID, compID, 'NAME')); 4println('Unit: ' + getAttrProperty(attributeID, compID, 'UNIT_NAME')); 5println('Symbol: ' + getAttrProperty(attributeID, compID, 'SYMBOL')); 6println('Value: ' + getAttrProperty(attributeID, compID, 'RDAT_VALUE'));
Assigns the component with ID 8 to the compID variable. | |
Assigns the ID of the face width attribute to the attributeID variable. | |
Outputs the name of the attribute to the scripting console. | |
Outputs the unit of the attribute to the scripting console. | |
Outputs the symbol of the attribute to the scripting console. | |
Outputs the output value of the attribute to the scripting console. |
Accessing components
getCompProperty()
getCompProperty(compID, propertyID); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
compID | int | Unique ID of the component in the model |
propertyID | string | TYPE - component type (e.g., cylindrical_mesh) |
NAME - component name | ||
Return value | string | Property of the component |
Possible errors | Incorrect component ID | |
Example 1 Output a component name and type to the scripting console.
1var compID = 3; 2println(getCompProperty(compID,'TYPE')); 3println(getCompProperty(compID,'NAME'));
Assigns a value of 3 to the compID variable. | |
Outputs the component type of component 3 to the scripting console. | |
Outputs the component name of component 3 to the scripting console. |
Notice
In earlier versions of the FVA-Workbench, the properties IDENT_NO and DRAWING_NO could be queried via getCompProperty().
The drawing number (comp_drawing_number) and Ident number (comp_ident_number) are now attributes of the respective component and can be set or read via setAttr() and getAttr().
Example for reading the number of a drawing: getAttr("comp_drawing_number", 3, EDAT);
setCompProperty()
setCompProperty(compID, propertyID); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
compID | int | Unique ID of the component in the model |
propertyID | string | NAME - name of the component |
Possible errors | Incorrect component ID | |
Example Change the name of a component.
var compID = 3; setCompProperty(compID, "NAME", "New component name");
getCompByType()
getCompProperty(compType); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
compType | string | Component type (e.g., "bearing") |
Return value | array | Array of component IDs |
Possible errors | Component type does not exist. | |
Example 1 Set the input type for all rolling bearings in the model to "rigidity."
1let bearings = getCompByType("bearing"); 2for (i=0; i < bearings.length; i++){ 3 setAttr("bearing data type", bearings[i], 2, EDAT); }
Assigns the variable bearings with an array of all rolling bearing IDs in the gear unit. | |
for loop that runs once for each element in the array. | |
Sets the attribute "input type " for each bearing to "rigidity" (value =2, see data type: combo attributes). |
getSubComponents()
getSubComponents(compID, subCompType); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
compID | int | ID of the main component |
subCompType | string | Component type of the sub-component to be queried e.g., "cylindrical_mesh". |
Return value | array | Array of the ID's of the sub-components. If there are no sub-components, an empty array will be returned. |
Possible errors | The queried component type does not exist on the main component. The main component does not exist. | |
Example 1 Query a cylindrical stage
1var stageID = 3; 2var gearIDs = getSubComponents(stageID, "general_gear"); 3println(gearIDs[0]); 4println(gearIDs[1]);
Variable stageID includes the ID of the cylindrical stage. | |
getSubComponents() writes an array with the ID's of both cylindrical gears to the gearIDs variable. | |
Writes the ID of the first cylindrical gear to the console. | |
Writes the ID of the second cylindrical gear to the console |
Querying sub-components
Component | Exactly what is queried | getSubComponents(...) |
|---|---|---|
Gears | All gears in a stage | stageID, "general_gear" |
Specific gear type, e.g. bevel gear | stageID, "bevel_or_hypoid_gear" | |
Shafts | All shafts in a stage | stageID, "shaft" |
Component | Exactly what is queried | getSubComponents(...) |
|---|---|---|
Modification | Modification for certain gear types. | gearID, "gear_correction" |
Shaft | Shaft on which the gear sits. | gearID, "shaft" |
Mating gears | All mating gears that mesh with the gear. | gearID, "general_gear" |
Stages | All stages in which the gear appears. | gearID, "general_stage" |
Stage-related gear data | Abstract component that includes the mesh-related data of a gear (e.g., pitch diameter). | gearID, "stage_gear_data" If a gear is engaged in multiple meshes, returns a component of type stage_gear_data for each mesh. |
gearID, "stage_gear_data", "STAGEID=3" If the ID of the stage is given as an option (here, a stage with ID 3), only the component of type stage_gear_data that belongs to the specified stage is returned. |
Component | Exactly what is queried | getSubComponents(...) |
|---|---|---|
Stages | All stages in which the shaft is present. | shaftID, "general_stage" |
Gears | All gears on the shaft | shaftID, "general_gear" |
Specific gear type, e.g., bevel gear | shaftID, "bevel_or_hypoid_gear" | |
Rolling bearings | All rolling bearings connected with the shaft. | shaftID, "bearing", "ANY" |
Rolling bearings that sit on the shaft. | shaftID, "bearing", "OUTER" | |
Rolling bearings that sit in the shaft. | shaftID, "bearing", "INNER" | |
Plain bearings | All plain bearings connected with the shaft | shaftID, "slide_bearing", "ANY" |
Plain bearings that sit on the shaft. | shaftID, "slide_bearing", "OUTER" | |
Plain bearings that sit in the shaft. | shaftID, "slide_bearing", "INNER" | |
Load | All load components (forces) on the shaft | shaftID, "force" |
Notch | All notches on the shaft | shaftID, "notch" |
Shaft contour | All contours | shaftID, "contour", "ANY" |
All outer contours | shaftID, "contour", "OUTER" | |
All inner contours | shaftID, "contour", "INNER" | |
Feather key | All feather keys on the shafts | shaftID, "feather_key", "ANY" |
All feather keys for which the shaft is the inner part. | shaftID, "feather_key", "INNER" | |
All feather keys for which the shaft is the outer part. | shaftID, "feather_key", "OUTER" | |
Tapered interference fit | All tapered interference fits on the shaft | shaftID, "cone_interference_fit", "ANY" |
All tapered interference fits for which the shaft is the inner part. | shaftID, "cone_interference_fit", "INNER" | |
All tapered interference fits for which the shaft is the outer part. | shaftID, "cone_interference_fit", "OUTER" | |
Multiple interference fit | All multiple interference fits on the shaft | shaftID, "multiple_interference_fit", "ANY" |
All multiple interference fits for which the shaft is the inner part. | shaftID, "multiple_interference_fit", "INNER" | |
All multiple interference fits for which the shaft is the outer part. | shaftID, "multiple_interference_fit", "OUTER" | |
Cylindrical interference fit | All cylindrical interference fits on the shaft | shaftID, "interference_fit", "ANY" |
All cylindrical interference fits for which the shaft is the inner part. | shaftID, "interference_fit", "INNER" | |
All cylindrical interference fits for which the shaft is the outer part. | shaftID, "interference_fit", "OUTER" | |
Spline connection | All spline connections on the shaft | shaftID, "spline_connection" |
All spline shafts on the shaft | shaftID, "spline_shaft" | |
All spline hubs on the shaft | shaftID, "spline_hub"Ko | |
Coupling | All couplings on the shaft | shaftID, "clutch" |
Component | Exactly what is queried | getSubComponents(...) |
|---|---|---|
Connected components | All components connected with the rolling bearings | bearingID, "default", "ANY" |
Components connected with the inner ring (shafts or casings) | bearingID, "shaft", "INNER" bearingID, "gear_casing" ,"INNER" | |
Components connected with the outer ring (shafts or casings) | bearingID, "shaft", "OUTER" bearingID, "gear_casing" ,"OUTER" | |
Bearing rows | Bearing rows are result components that can only be queried after a successful calculation. | bearingID, "bearing_row" |
Component | Exactly what is queried | getSubComponents(...) |
|---|---|---|
Connected components | All components connected with the plain bearing | slideBearingID, "default", "ANY" |
Components connected with the inner ring (shafts or casings) | slideBearingID, "shaft", "INNER" slideBearingID, "gear_casing" ,"INNER" | |
Components connected with the outer ring (shafts or casings) | slideBearingID, "shaft", "INNER" slideBearingID, "gear_casing" ,"INNER" | |
Segments | Segments, hydrostatic and hydro dynamic pockets are result components that can only be queried after a successful calculation. | slideBearingID, "slide_bearing_segment" |
Hydrostatic pockets | slideBearingID, "hydrostatic_pocket" | |
Hydrodynamic pockets | slideBearingID, "hydrodynamic_pocket" |
Component | Exactly what is queried | getSubComponents(...) |
|---|---|---|
Cylindrical gear stages | All cylindrical stages in the planetary stage | planetaryStageID, "general_stage" |
Only the inner stage | planetaryStageID, "general_stage", "INNER" | |
Only the outer stage | planetaryStageID, "general_stage", "OUTER" | |
Gears | All gears in the planetary stage | planetaryStageID, "general_gear" |
Sun gear | planetaryStageID, "general_gear", "SUN_GEAR" | |
Planet gear | planetaryStageID, "general_gear", "PLANET_GEAR" | |
Ring gear | planetaryStageID, "general_gear", "RING_GEAR" | |
Shafts | All shafts in the planetary stage | planetaryStageID, "shaft" |
Sun shaft | planetaryStageID, "shaft", "SUN_SHAFT" | |
Planet shaft | planetaryStageID, "shaft", "PLANET_SHAFT" | |
Ring shaft | planetaryStageID, "shaft", "RING_SHAFT" | |
Carrier shaft | planetaryStageID, "shaft", "RIM_SHAFT" | |
Planet carrier | One-sided planet carrier | planetaryStageID, "one_sided_planet_carrier" |
Two-sided planet carrier | planetaryStageID, "two_sided_planet_carrier" | |
Pins | planetaryStageID, "planet_pin" | |
Instances | Cylindrical gear stage in the planetary stage | stageID, "planet_instance" |
Planetary gear | planetGearID, "planet_instance" | |
Planet carrier | planetBearingID, "planet_instance" | |
Pins | planetPinID, "planet_instance" | |
Coupling | couplingID, "planet_instance" |
Component | Exactly what is queried | getSubComponents(...) |
|---|---|---|
Notch | Shaft on which the notch is located. | notchID, "shaft" |
Load | Shaft on which the load component is located. | forceID, "shaft" |
Spline connection | Shafts that are connected to each other by the spline connection. | splineConnectionID, "Shaft" |
Gears that make up the spline connection. | splineConnectionID, "general_gear" |
addSubComponent()
addSubComponent(baseCompID, compType, {options}); | |||
Parameter | Type | Description | |
baseCompID | int | ID of the primary component to which the sub-component should be added. | |
compType | string | Component type of the sub-component to be added. The following types are available:
| |
{options} | object | The following additional options are available for shaft contours. If no options are specified, shaft sections are added as outer contours from the left. | |
Shaft inner/outer contour | side: inner/outer | ||
Specification of shaft contour from left/right | direction: left/right | ||
Return value | int | ID of the newly added component | |
Possible errors | The primary component does not exist. The sub-component type cannot be added to the primary component. | ||
Note
Adding or deleting components may take some time, especially for large models, as the 3D model is updated each time.
Transaction mode can be enabled before the addSubComponent() call to speed up the process.
Example 1 Add a notch on a shaft and assign the basic attributes
1let shaftID = 3; 2let notchID = addSubComponent(shaftID, "notch"); 3setAttr("notch kind", notchID, 6, EDAT); 4setAttr("position", notchID, 6, EDAT); 5setAttr("notch width", notchID, 5, EDAT); 6setAttr("notch radius", notchID, 2, EDAT); 7setAttr("depth", notchID, 2, EDAT); 8setAttr("surface roughness", notchID, 10, EDAT);
The shaftID variable includes the ID of the shaft on which the notch should be added. | |
Adds a new component of type "notch" on shaft 3 via addSubComponent(). The return value of the function, the ID of the new notch, is saved in the notchID variable. | |
Sets the "notch form" combo attribute for the new notch to 6 via setAttr(). The value 6 corresponds to a rectangular notch. (See image for additional options) 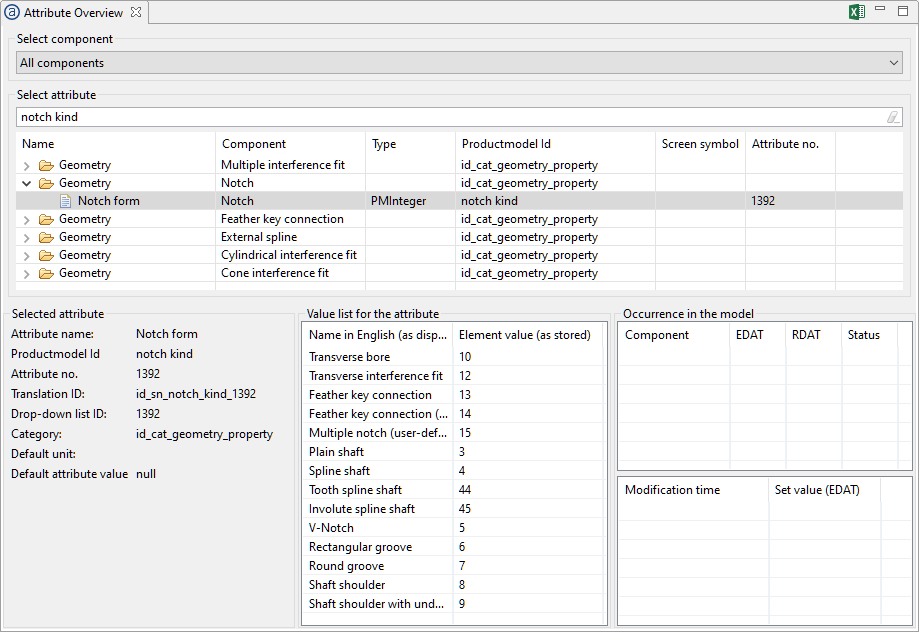 | |
Sets the position of the notch. | |
Sets the width of the notch. | |
Sets the radius of the notch. | |
Sets the depth of the notch. | |
Sets the surface roughness R_z of the notch. |
Example 2 Add a contour to an existing shaft
var shaftID = 3;
var nbrOuterContours = 3;
var nbrInnerContours = 2;
var outerContourIDs = [];
var innerContourIDs = [];
var outerContourlenght = [30, 50, 20];
var innerContourlenght = [40, 80];
var outerContourDiameters = [30, 50, 25];
var innerContourDiameters = [10, 20];
for (let i = 0; i < nbrOuterContours; i++){
let options = {};
outerContourIDs.push(addSubComponent(shaftID, "contour",{side: "outer", direction: "left"}));
}
for (let i = 0; i < nbrInnerContours; i++){
innerContourIDs.push(addSubComponent(shaftID, "contour",{side: "inner", direction: "left"}));
}
for(let i = 0; i < nbrOuterContours; i++){
setAttr("length", outerContourIDs[i], outerContourlenght[i], EDAT);
setAttr("beginning diameter", outerContourIDs[i], outerContourDiameters[i], EDAT);
setAttr("end diameter", outerContourIDs[i], outerContourDiameters[i], EDAT);
}
for(let i = 0; i < nbrInnerContours; i++){
setAttr("length", innerContourIDs[i], innerContourlenght[i], EDAT);
setAttr("beginning diameter", innerContourIDs[i], innerContourDiameters[i], EDAT);
setAttr("end diameter", innerContourIDs[i], innerContourDiameters[i], EDAT);
}deleteSubComponent()
deleteSubComponent(baseCompID, compID); | |||
Parameter | Type | Description | |
baseCompID | string | ID of the primary component from which the sub-component should be deleted. | |
compType | string | ID of the component to be deleted. | |
Possible errors | The primary component does not exist. The sub-component does not exist. | ||
Example Delete a load component from a shaft
var shaftID = 4; var forceID = 10; deleteSubComponent(shaftID, forceID);
addDbComponent()
addDbComponent(dbType, entryId); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
dbType | string | Type of the database component to be added.
|
entryId | string | Unique ID of the database component in the database. |
Return value | string | ID of the newly added component |
Possible errors | Incorrect database type Database entry does not exist | |
Example Add the material 16MnCr5 as a component to the model and allocate it to a cylindrical gear
gearID = 8;
var materialID = addDbComponent("material", "16MnCr5");
setAttr("material", gearID, materialID, EDAT);deleteDbComponent()
deleteDbComponent(compId); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
compId | string | ID of the database component to be deleted. |
Possible errors | Database component does not exist in the model. | |
Example Delete the database component with the ID 120
deleteDbComponent("120");refreshDbComp()
refreshDbComp(dbCompID); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
dbCompID | int | Unique ID of the database component in the model |
Possible errors | Database component does not exist in the model. |
Example 1 Update the component with the ID 22 with data from the Global Database.
refreshDbComp(22);
Output
generateReport()
generateReport(templateFile, outputFile, {options}); | |||
Parameter | Type | Description | |
templateFile | string | Path + name of the report template file | |
outputFile | int | Path + name of the HTML file | |
{options} | object | Single-column layout | compactView:true/false |
Language | language: "de"/"en" | ||
Hierarchical model tree | completeTree: true/false | ||
Navigation bar | navigationBar: true/false | ||
Calculation messages | notifications: true/false | ||
Possible errors | Access restrictions on folders/files Missing report template | ||
Notice
The getPredefinedReportTemplate(SYSTEM_REPORT); feature can be used to query the path to the pre-defined "system report" template.
Example 1 Generate an HTML report
1var templateFile = "C:\\template.wbrep"; 2var outputFile = "C:\\output\\report.html"; 3var options = {compactView: false, language: "de", completeTree: false, notifications: true, navigationBar: true}; 4generateReport(templateFile, outputFile, options);
Path to report template | |
Path where the output report will be generated | |
Options to be considered when generating the report | |
Function for generating the report |
Example 2 Create an HTML report with the pre-defined system report template
var templateFile = getPredefinedReportTemplate(SYSTEM_REPORT); var outputFile = "C:\\output\\report.html"; generateReport(templateFile, outputFile);
println()
println(data); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
data | any | Data to be output to the scripting console. |
Possible errors | Missing Component ID Missing Attribute ID | |
Example 1
1var text = "This is text"; 2var array = [1, 2.2, 3, 4]; 3println(text); for (i=0; i<array.length; i++){ 4 println(array[i]); }
alert()
alert(data); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
data | any | Text or data to be shown in the dialog. |
Example 1 Output text as a message.
var text = "This is a message. Click OK to continue." alert(text);
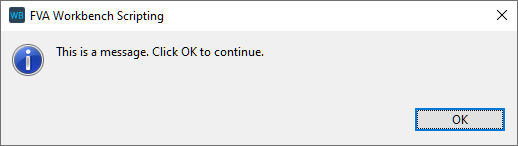
Example 2 Output multiple messages in a loop.
1for (i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 2 alert("This is the " + i + ". run"); }
User input
prompt()
prompt(data); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
data | any | Text or data to be displayed as text in the input dialog. |
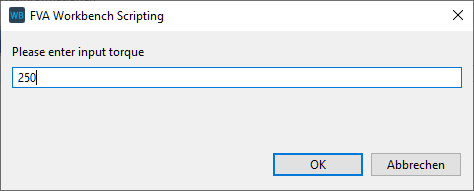
Example 1 Request torque from the user and set the attribute value of the load component accordingly.
1var forceID = 20; 2var torque = prompt("Please enter input torque"); 3setAttr("scaled torque", forceID, torque, EDAT);
Assigns the variable forceID with the ID of a load component. | |
Writes the return value of the prompt() function to the torque variable. | |
Sets the input value (EDAT) of the torque attribute for load component 20 to the value in specified in the dialog box. |
promptFile()
promptFile({options}) | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
{options} | object | directory - default file path filename - suggested file name type - type of dialog: open ("open") or save ("save"). Default: "open" |
Note
This function can only be used in GUI operation, not in batch operation.
Example 1 Write text to a file selected by the user.
1let options = {directory: "c:/example", filename: "myfile.txt", type: "save"}; 2let path = promptFile(options); 3let text = "This Text will be written to the ASCII File"; 4writeToFile(path, text, "c", "UTF-8");
promptDirectory()
promptDirectory(baseDirectory); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
data | string | Specification of a predefined path If no parameter is specified, the most recently selected directory is displayed. |
Note
This function can only be used in GUI operation, not in batch operation.
Example 1 Write a text file to a user-selected directory.
1let directory = promptDirectory("c:/example"); 2let filename = "text.txt"; 3let path = directory +"/"+ filename; 4let text = "This Text will be written to the ASCII File"; 5writeToFile(path, text, "c", "UTF-8");
Opens a directory selection dialog and writes the selected path to the directory variable. C:\example is selected by default. | |
Stores the name of the output file in the filename variable. | |
Assembles the strings into a complete file path and stores it in the path variable. | |
Text to be written in the output file. | |
Writes the text to the specified file. |
promptSelect()
promptFile(baseDirectory) | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
caption | string | Text shown above the drop down list |
dropDownEntries | array of strings | Array of strings: each string corresponds to an entry in the drop down list. |
Note
This function can only be used in GUI operation, not in batch operation.
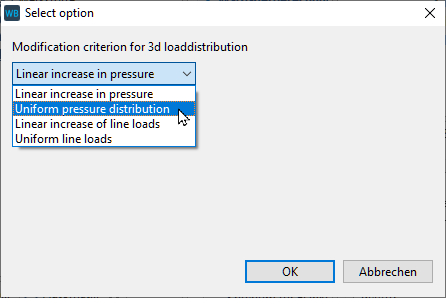
Example 1 Query the user for criteria for the proposed modification and set the corresponding attribute in the FVA-Workbench.
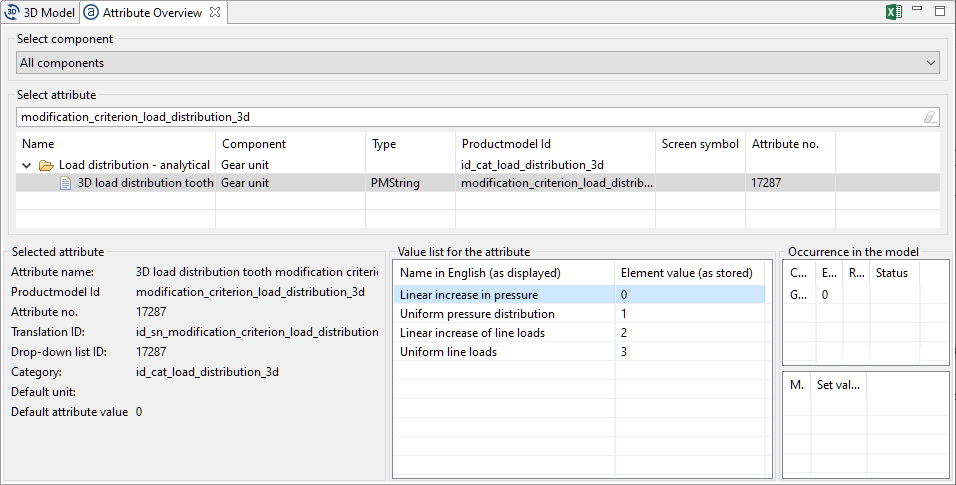
The possible values for the "3D load distribution tooth modification criterium" combo attribute can be seen in the attribute overview.
1let dropDownEntries = [ "Linear increase in pressure", "Uniform pressure distribution", "Linear increase of line loads", "Uniform line loads" ]; 2let modCriterion = promptSelect("Select modification criterion for 3d loaddistribution", dropDownEntries); 3switch (modCriterion) { case "Linear increase in pressure": modCriterion = "0"; break; case "Uniform pressure distribution": modCriterion = "1"; break; case "Linear increase of line loads": modCriterion = "2"; break; case "Uniform line loads": modCriterion = "3"; break; default: break; }; 4setAttr("modification_criterion_load_distribution_3d", 1, modCriterion, EDAT);
Writes the selection options for the drop-down menu as a string array to the dropDownEntries variable. | |
Opens the drop-down dialog; the return value is written to the modCriterion variable. | |
The switch case statement assigns a valid value for the "modification_criterion_load_distribution_3d" attribute to the strings selected by the user. | |
Sets the input value for the "modification_criterion_load_distribution_3d" attribute in the FVA-Workbench. |
Export
exportModel()
exportModel(fileName, {options}); | ||||
Parameter | Type | Description | ||
fileName | string | Path + name of the model file. The following file extensions are supported: .wbpz .wbpx .wbps .rexs (xml) .rexsj (json) | ||
{options} (Only for REXS export) | object | DataClass Determines whether EDAT or RDAT should be written. If the RDAT data is not valid, EDAT will automatically be written. (EDAT/RDAT) | Version Specifies the version of the REXS specification to be used. (1.0/1.1/1.2/1.3/1.5) | |
Possible errors | The user does not have write permissions to the specified directory. | |||
Example 1 Export the file model.wbpz to the C:\temp directory.
exportModel("C:\\temp\\model.wbpz");
Example 2 Export the model in REXS format (version 1.3)
1var options = {DataClass: "RDAT", Version: 1.3}; 2exportModel("C:\\temp\\model.rexs", options);
exportCAD()
exportCAD(filepath, {options}); | |||
Parameter | Type | Description | |
filepath | string | Path + name of the CAD file | |
{options} | object | CompIds | Assembled components such as cylindrical stages cannot be exported. The shafts and gears of the stage must be explicitly specified for the export. A list of all gearbox components to be exported. ID = 1 (gear unit) exports the entire gearbox model. Duplicate IDs are ignored. |
CADFormat | The following formats can be exported:
| ||
Possible errors | The user does not have write permissions to the specified path. The specified component cannot be exported (e.g., lubricant). | ||
Example 1 Export the complete gearbox as a STEP file
let filepath = "c:/output/cadmodel.step";
let options = {"CompIds": [1],
"CADFormat": "STEP"
};
exportCAD(filepath, options);Example 2 Export all shafts and gears of a gearbox model as an IGES file
let filepath = "c:/output/cadmodel.iges";
let gearIds = getCompByType("gear");
let shaftIds = getCompByType("shaft");
let componentsToExport = gearIds.concat(shaftIds);
let options = {"CompIds": componentsToExport,
"CADFormat": "IGES"
};
exportCAD(filepath, options);exportCADGear()
exportCADGear(filepath, {options}); | |||
Parameter | Type | Description | |
filepath | string | Path + name of the CAD file | |
{options} | object | CompId | ID of the cylindrical gear |
CADFormat | The following formats can be exported:
| ||
NumberOfSupportingPointsWidth | The number of supporting points in the width direction is equidistant and has a significant influence on the accuracy with which the flank modifications can be exported. The accuracy of the linear interpolation between the support points depends on the shape and amount of the modification. For example, if a short end relief with a large modification amount is to be specified, the number of support points should be increased. | ||
Possible errors | The user does not have write permissions to the specified path. The specified component is not a cylindrical gear. | ||
Example Export a cylindrical gear, including modifications
let filepath = "c:/output/cadmodel.step";
let gearId = [6];
let options = {"CompId": gearId,
"CADFormat": "STEP",
"NumberOfSupportingPointsWidth": 20
};
exportCADGear(filepath, options);exportImage()
exportImage(filepath, {options}); | |||||||||
Parameter | Type | Description | |||||||
filepath | string | Path + name of the image file | |||||||
{options} | object | CompIds | List of all transmission components that should be included in the image. ID = 1 (gear unit) exports the entire gear model as an image. Duplicate IDs are ignored. Composite components such as gear stages cannot be exported as an image. The shafts and gears of the stage must be explicitly specified for export. | ||||||
size | Image resolution
| ||||||||
orientation | Orientation of the transmission components in the picture.
| ||||||||
showDeformation | Boolean that decides whether the gear components are displayed deformed. | ||||||||
Possible errors | The user does not have write permissions to the specified path. The specified component cannot be exported as image (e.g., lubricant). | ||||||||
Example 1 Export the complete gearbox as an image file
let filepath = "c:/output/transmission.jpg";
let options = {"CompIds": [1],
"orientation" : "ISO",
"size": "SMALL",
"showDeformation": true
};
exportImage(filepath, options);Example 2 Export all shafts and gears of a gear model as an image file
let filepath = "c:/output/shafts_and_gears.jpg";
let gearIds = getCompByType("gear");
let shaftIds = getCompByType("shaft");
let componentsToExport = gearIds.concat(shaftIds);
let options = {"CompIds": componentsToExport,
"orientation" : "ISO",
"size": "LARGE",
"showDeformation": false
};
exportImage(filepath, options);Read & Write
readFile()
readFile(path); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
path | string | Path + name of the file |
Return value | array | Contents of the file in a string array |
Possible errors | File does not exist or access is denied. File is in binary format. | |
Example 1 Import a text file and output it to the scripting console
1var path = "c:\\textfile.txt"; 2var text = readFile(path); 3for (i = 0; i < text.length; i++){ 4 println(text[i]); 5 println(parseFloat(text[i])+ parseFloat(text[i])); }
Assigns the path variable with the path to the text file. | |
Uses readFile() to assign the text variable with an array with a number of entries equal to the number of lines in the textfile.txt file. | |
For loop which increases the counting variable i from 0 to text.length (number of lines in the text file). | |
Outputs every line of the text file to the scripting console. | |
Uses parseFloat() to convert every array entry in the text variable to a floating point number which can then be used for further calculations. If the array entry does not contain a number that can be converted, parseFloat() returns NaN (Not a Number) as a value. |
readFileAsString()
readFileAsString(path); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
path | string | Path + name of the file |
Return value | string | Content of the file in a string |
Possible errors | File does not exist or access is denied. File is in binary format. | |
Example 1 Read text file as string
1var path = "c:\\textfile.txt"; 2var text = readFileAsString(path);
writeToFile()
writeToFile(path, text, mode, encoding); | ||||
Parameter | Type | Description | ||
path | string | Path + name of the text file Relative paths can also be specified. In this case, the parent directory is the directory where the FVA-Workbench is installed. | ||
text | string | Text to be written to the file | ||
mode | string | a Adds the text to an existing file. The file will be created if necessary. | c If the file already exists, the contents will be replaced. Otherwise, the system will create the file and add the text. | |
encoding | string | If no parameters are specified, the default encoding of the operating system is used. It is recommended to specify the encoding to ensure compatibility between different systems. UTF-8 UTF-16BE UTF-16LE UTF-16 ISO-8859-1 US-ASCII BINARY | ||
Possible errors | The user does not have write permissions to the specified path. | |||
Example Create a text file and add additional text.
1var path = "C:\\temp\\test.txt"; 2writeToFile(path, "Part 1\n", "c", "UTF-8"); 3writeToFile(path, "Part 2\n", "a", "UTF-8"); 4writeToFile(path, "Part 3", "c", "UTF-8");
saveModel()
saveModel(); | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
Possible errors | Access to the model file is denied. | |
Example 1 Save the model file
saveModel();
Additional
#include
#include "path\\script.wbjs"; | ||
Parameter | Type | Description |
Possible errors | The specified script file or path does not exist The file extension is not .wbjs | |
Notice
For more examples, see Embedding external scripts
Example 1 Include external scripts
1#include "*"; 2#include "folder\\*"; 3#include "folder\\script.wbjs"; 4#include "c:\\scripting\\folder\\script.wbjs"
getModelProperty();
getModelProperty(propertyID); | |||||
Parameter | Type | Description | |||
propertyID | string | FILEPATH | Complete path to the model file. | c:/example/modelfolder/model.wbpz | |
FOLDER | Path where the model file is located. | c:/example/modelfolder/ | |||
FILENAME | Name of the model file. | model.wbpz | |||
FILENAME_NO_EXT | Name of the model file without file extension. | model | |||
MODEL_NAME | Name of the project or model. Project name can be changed under Project -> Properties | Twin-Screw Extruder | |||
PM_VERSION | Product model version | 2.2169.0 | |||
Example 1 Write a text file to a subdirectory of the model folder.
1let modelpath = getModelProperty("FOLDER"); 2let modelname = getModelProperty("MODEL_NAME"); 3let filepath = modelpath + "new_directory/textfile.txt"; 4writeToFile(filepath, modelname, "c", "UTF-8");
Assigns the path of the model file to the modelpath variable. | |
Assigns the name of the model to the modelname variable. | |
Appends the string "new_directory/textfile.txt" to the modelpath variable and writes it to the filepath. | |
Writes a text file that includes the model name as text to the path of the filepath variable. |
getDirectory()
getDirectory(folderID); | |||||
Parameter | Type | Description | |||
folderID | string | global_scripts | global scripts | ||
models | preferred location for saving gearbox models | ||||
temp | temporary files | ||||
report_templates | report templates | ||||
reports | preferred output folder for reports | ||||
Example Query the directory for report templates and the output folder and create a results report.
1let reportTemplateDirectory = getDirectory("report_templates"); 2let templateFile = reportTemplateDirectory +"\\myReportTemplate.wbrep"; 3let outputDirectory = getDirectory("reports"); 4let outputFile = outputDirectory+"\\report.html"; 5generateReport(templateFile, outputFile); 6println("Report was saved here: "+outputFile);
Queries the path in which the .wbrep report templates are located and saves it to the reportTemplateDirectory variable | |
Appends the name of the report template to reportTemplateDirectory and saves it to the templateFile variable. | |
Queries the path in which the .html results reports are saved by default and saves it to the outputDirectory variable. | |
Appends the names of the output reports to outputDirectory and saves them to the outputFile variable. | |
Creates a report. | |
Outputs the location of the output report to the Scripting Monitor. |